🇦🇷🇨🇳 Milei’s Strategy to Confront China and Its "Axis of Dictators"
Today we will understand how Argentina, when under the control of the Foro de São Paulo, was an important asset for the Chinese Communist Party in South America and how Javier Milei is charting paths to change this scenario.
The Chinese government has been making diplomatic overtures to areas near the polar regions as part of its maritime strategy.
After a "strategic retreat," the Southern Hemisphere has assumed a new dimension for Chinese interests in South America.
Beijing has been increasing its diplomatic engagement with countries in the region, especially Argentina in recent times, through a series of economic, sociocultural, and to a lesser extent, military agreements. This includes the delivery of vaccines and the intention to accelerate an investment plan worth $30 million.
China has focused on several geopolitically sensitive projects in Argentina, all strategic: controlling air and maritime space and strategic facilities in territorial areas monitored by Beijing over Antarctica and the South Atlantic. However, doubts arise about China's intentions...
For Xi Jinping's government, Argentina stands out for its strategic location, the influential posture of its leaders, and its alignment with China's economic and military power expansion. China has made significant investments and infrastructure initiatives in various Argentine regions.
In addition to establishing a presence in the province of Neuquén, China has targeted the port city of Ushuaia in Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica, the South Atlantic islands, and the San Juan region near the Chilean border.
A 2012 agreement between authorities in Argentina's Neuquén province and Beijing allowed the construction of a deep space tracking station near the Chilean border, which caught Washington's attention.
In 2014, through a bilateral agreement between the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, represented by the Satellite Launch and Tracking Control General (CLTC) of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) and Argentina's National Commission on Space Activities (CONAE), the agreement identified the Argentine space station at Bajada del Agrio as the most favorable location for hosting a Chinese base in the Southern Hemisphere.
The project became operational in 2017 on a 200-hectare area and represents the third in a global network and the first outside China. It features a 110-ton, 35-meter-diameter antenna for deep space exploration (telemetry and technology for "terrestrial tracking, command, and data acquisition"), with the CLTC having a special exploration license for a period of 50 years.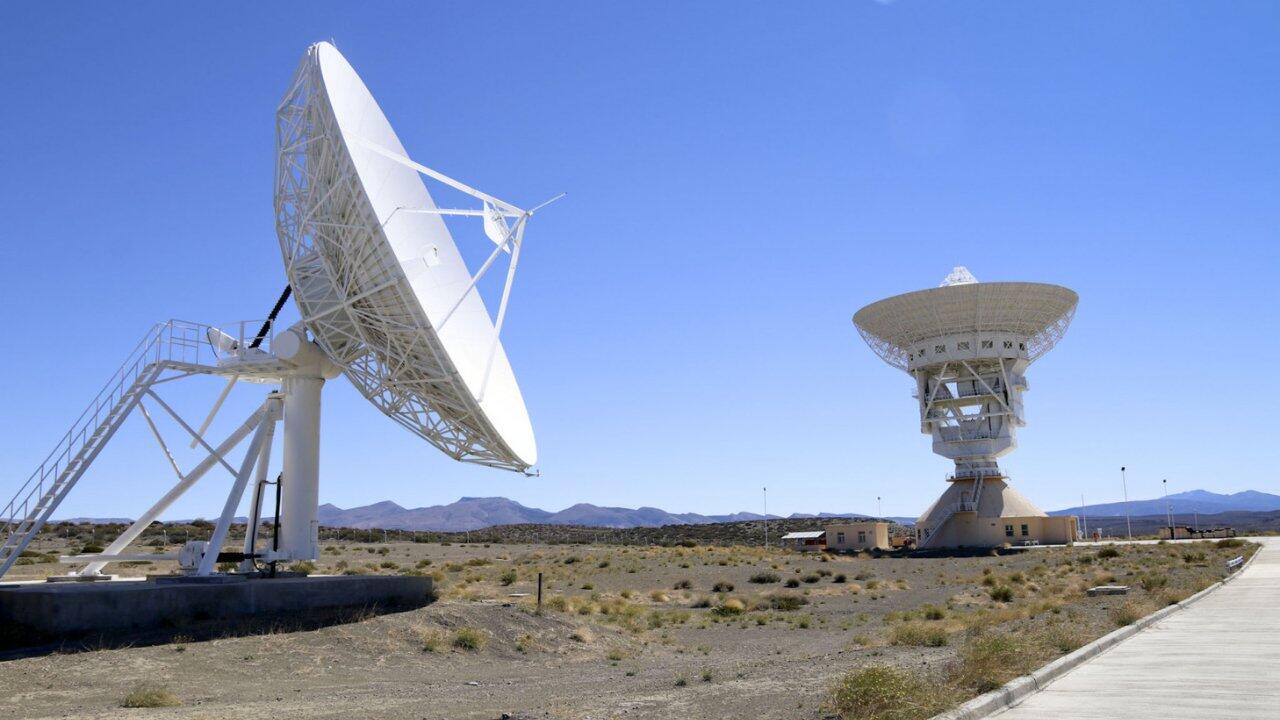
The 50-year contract grants the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) the ability to operate freely on Argentine soil. The facility, known as Espacio Lejano, set a precedent for a Chinese ground tracking station in Río Gallegos, on the southeastern coast of Argentina, which was formally announced in 2021.
In 2016, a document issued by the U.S. State Council Information Office raised concerns among the U.S. government and European Union (EU) countries about the potential military and geopolitical uses of the base in the Southern Hemisphere and Antarctica. Another element fueling suspicion is the existence of "secret clauses" in a document signed by the General Directorate of Legal Advisory (DICOL) of Argentina’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, International Trade, and Worship with the Chinese government.
Since the Espacio Lejano contract was signed, U.S. analysts and authorities have repeatedly expressed concern about China's growing collaboration with Argentina on security and surveillance issues.
In 2023, a general from the U.S. Southern Command stated during a hearing of the House Armed Services Committee: "The PRC [People's Republic of China] has expanded its capacity to extract resources, establish ports, manipulate governments through predatory investment practices, and build potential dual-use space facilities."
The shift in the Argentine government from a leftist spectrum, led by leaders of the São Paulo Forum, to a Milei administration, which has always advocated for libertarian and pro-Western rhetoric, has altered the dynamics of Chinese-Argentine relations in 2024.
Milei assumed office on December 10, 2023, replacing the progressive president Alberto Fernández, who had strengthened ties with China and signed an agreement in 2022 to join the CCP’s Belt and Road Initiative. During his campaign, Milei did not hide his disdain for communist regimes and signaled his intention to move away from socialist policies in favor of a more libertarian direction.
In the nearly seven months since taking office, Milei has implemented major economic reforms and streamlined the government.
Other recent "positive indicators" suggest that the Milei administration is prioritizing defense relations with the United States over China, according to Leland Lazarus, Associate Director of National Security at the Jack D. Gordon Institute for Public Policy at Florida International University.
"The fact is that, in just six months, he has already visited the United States several times. He has met with Secretary [Antony] Blinken, been to the White House... all of this is like absolute music to General Richardson's ears; to President [Joe] Biden's ears," Lazarus told Epoch Times.
General Richardson visited Argentina in April, a trip that included the donation of a C-130H Hercules transport aircraft to the Argentine Air Force and a visit to a naval facility in Ushuaia, Tierra del Fuego, at the southern tip of the country.
"We are committed to working closely with Argentina so that our collaborative security efforts benefit our citizens, our countries, and our hemisphere in enduring and positive ways," she said in a statement at the time.
In Ushuaia, General Richardson met with local military personnel to discuss their role in "safeguarding vital maritime routes for global trade."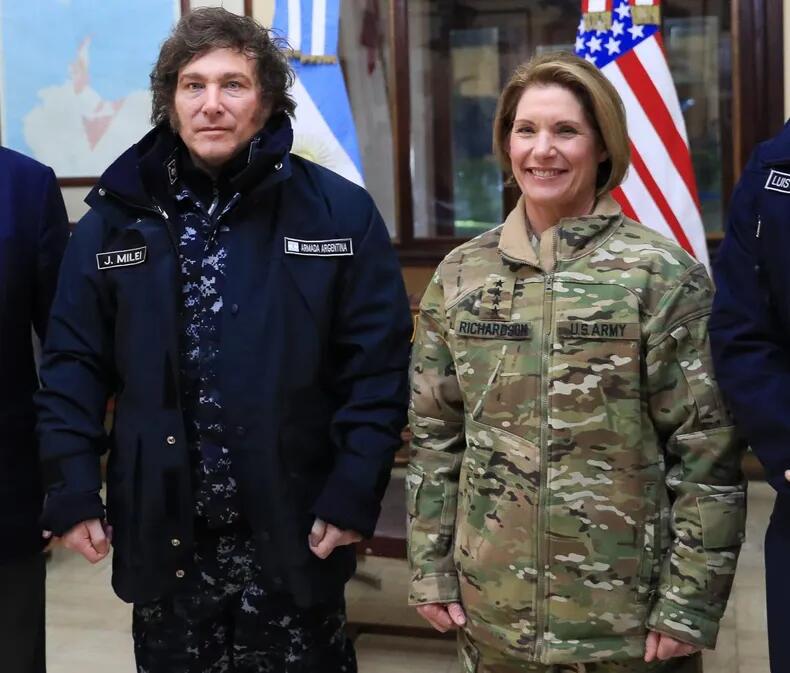
In a statement from the Argentine Ministry of Defense, Milei confirmed that General Richardson also reviewed the progress of an "integrated naval base" at the Ushuaia naval facility. Argentine officials said they also discussed "legislative modernization on defense issues."
Under the previous administration, China had received preferential treatment.
In June 2023, Tierra del Fuego Governor Gustavo Melella approved China's plans to build a "multi-use" port facility near the Strait of Magellan.
The project was met with legislative backlash, as three national deputies and members of the Civic Coalition filed an official complaint against the governor's provincial decree to build the port with Beijing. The same group also accused Melella of compromising Argentina’s national security.
No public records show that the project has progressed since then.
Argentina's desire for deeper security cooperation with Western partners was also evident in April when Argentine Defense Minister Luis Petri signed a historic agreement to purchase 24 F-16 fighter jets from Denmark.
"Today we are concluding the most important military aviation acquisition since 1983," Petri said in an official statement.
"Thanks to this investment in defense, I can proudly say that we are beginning to restore our air sovereignty and that our entire society is better protected against all the threats we face."
The purchase occurred after several media reports in 2022 indicated that the previous Fernández administration was considering buying JF-17 fighter jets made in China and Pakistan. A former minister from ex-president Mauricio Macri's government, who requested anonymity, confirmed to Epoch Times that a deal to acquire JF-17 jets was being considered during the Fernández era.
Chinese investment did not occur only in Argentina. According to a document from the U.S. House Foreign Affairs Committee: "From 2009 to 2019, China transferred a total of $634 million in significant military equipment to five South American countries—Argentina, Bolivia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela. The governments of Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Argentina purchased defense equipment from the PRC, cooperated in military exercises, and engaged in educational exchanges and training for their military personnel."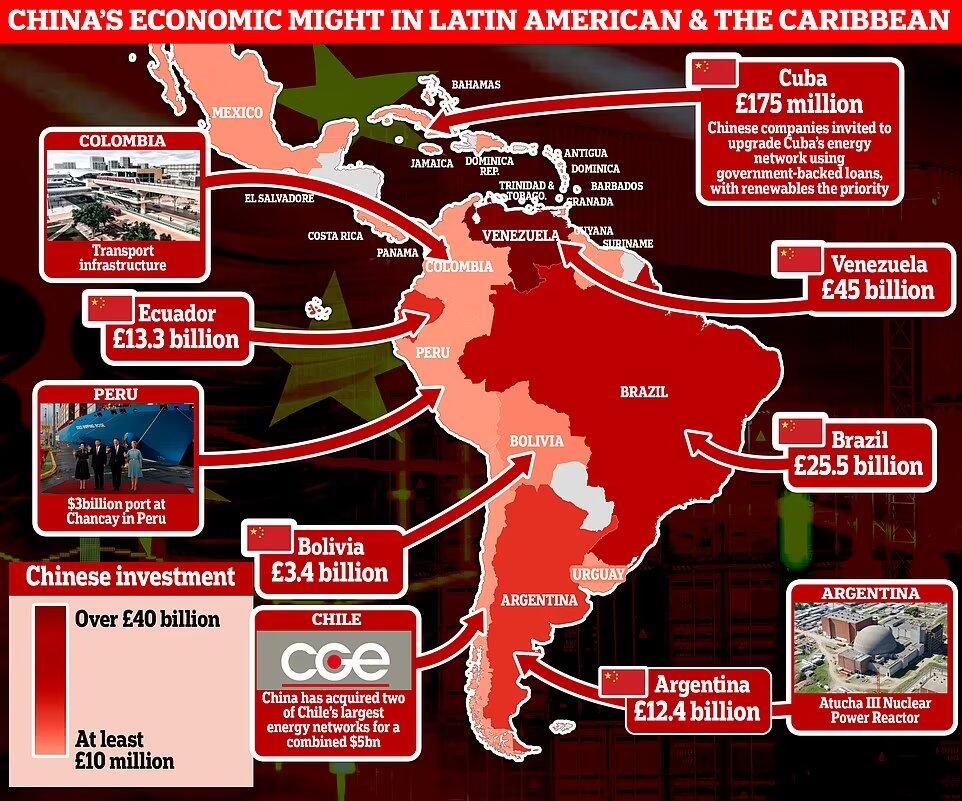
Access to space plays a crucial role in the CCP's strategic objectives.
Thus, when reports emerged in early April that Milei's government wanted to inspect Espacio Lejano, experts suggested it supported his national security moves away from China.
According to the Espacio Lejano contract, signed under Cristina Fernández de Kirchner's Peronist regime, CCP officials are not required to let anyone—including the Argentine president—enter the facility without prior notice.
According to Article 3, the agreement stipulates that Argentine authorities cannot interfere with or interrupt the "normal activities" of the facility and must explore alternative options and provide an unspecified amount of notice before being granted access.
China has maintained that Espacio Lejano is for deep space exploration, lunar missions, and communication with satellites already in orbit. However, there is deep skepticism that the claim of space exploration alone is highly unlikely.
The big question is: what could this facility do in times of war?
Neuquén is just one of 11 ground stations and space research facilities China has in Latin America and the Caribbean. This represents the largest concentration of space equipment China has outside its own country. According to data from the Gordon Institute, the Chinese Espacio Lejano station and the Río Gallegos facility provide an ideal surveillance position near the polar orbit.
The polar orbit is useful for data collection, transmission, and tracking because it allows for observation of the entire planet from space. The resolution of communications is also improved due to the proximity of satellites in orbit to the Earth's surface.
Additionally, it offers strategic advantages for any government involved in espionage.
Regarding deeper security collaboration with the United States, the trend is that Milei’s government will do as much as possible without jeopardizing its contracts with China, which is currently Argentina's second-largest trading partner.
However, if Argentina's defense cooperation with China cools, the communist regime might wait for another Argentine government to continue its expansion—a government that could be more favorable to the CCP's objectives.
Everything will depend on the continued success of Javier Milei's economic miracle, ensuring his government is re-elected and he can appoint a successor, making it more challenging for China, and avoiding a situation similar to what occurred in Brazil starting in 2023.

